AGEP vs GPP: When Skin Reactions Look Similar but Behave Very Differently Skin rashes can be alarming, especially when they appear suddenly and spread quickly. Two conditions that often cause confusion are acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) and generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP). AGEP vs GPP is a comparison that often raises confusion among both patients and clinicians. These two skin conditions can appear strikingly similar at first glance, yet their causes, clinical behavior, and long-term management are very different. Understanding these differences is important — not only for accurate diagnosis,…
Read MoreTag: drug allergy
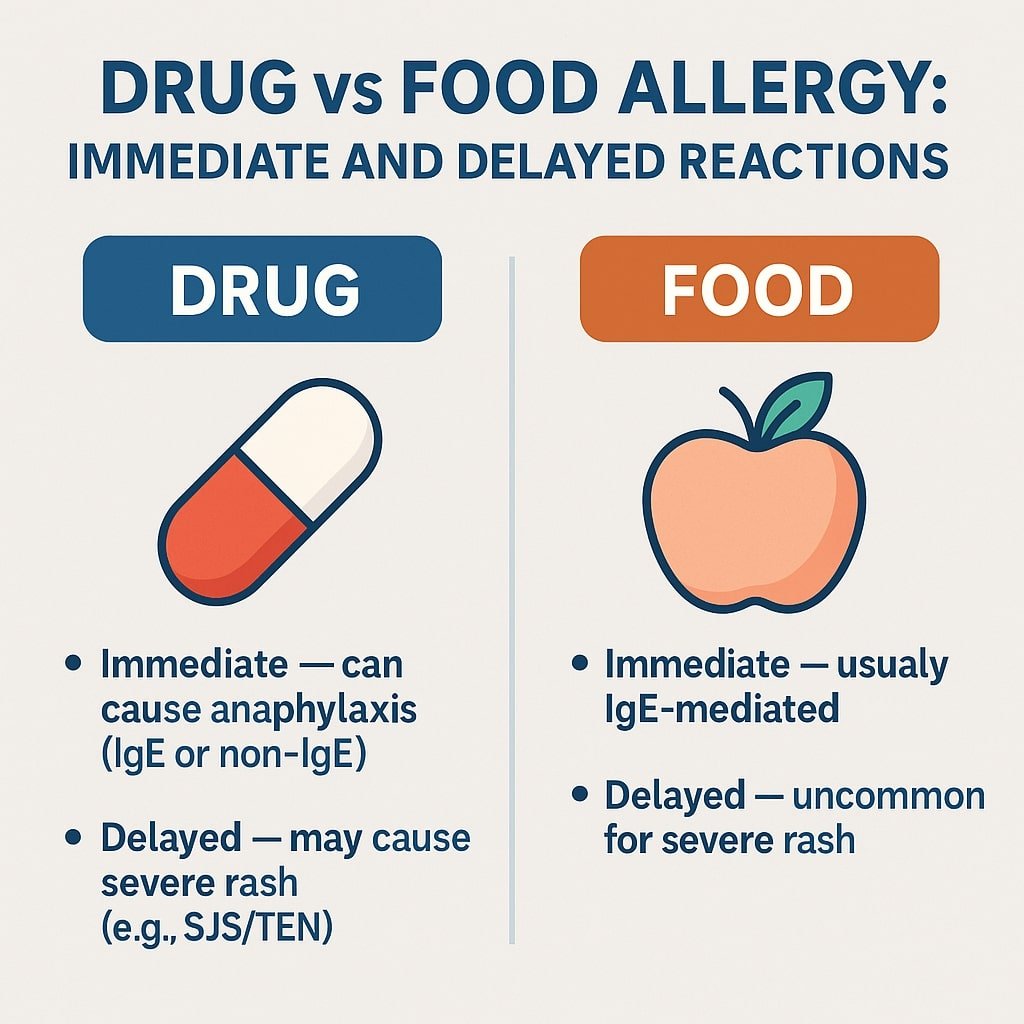
Drug vs Food Allergy: Immediate & Delayed Reactions
Drug vs Food Allergy: Why Medications Can Cause Both Immediate and Delayed Reactions — While Foods Uncommonly Cause Severe Delayed Reactions This article is for educational purposes only. Always consult healthcare providers for personalized medical advice. Patients often ask:“Why can medications cause both rapid allergic reactions like hives or anaphylaxis and dangerous delayed reactions such as Stevens–Johnson Syndrome (SJS) or Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), while food allergies almost always appear immediately?” The difference lies in how the immune system processes drugs versus foods — and in…
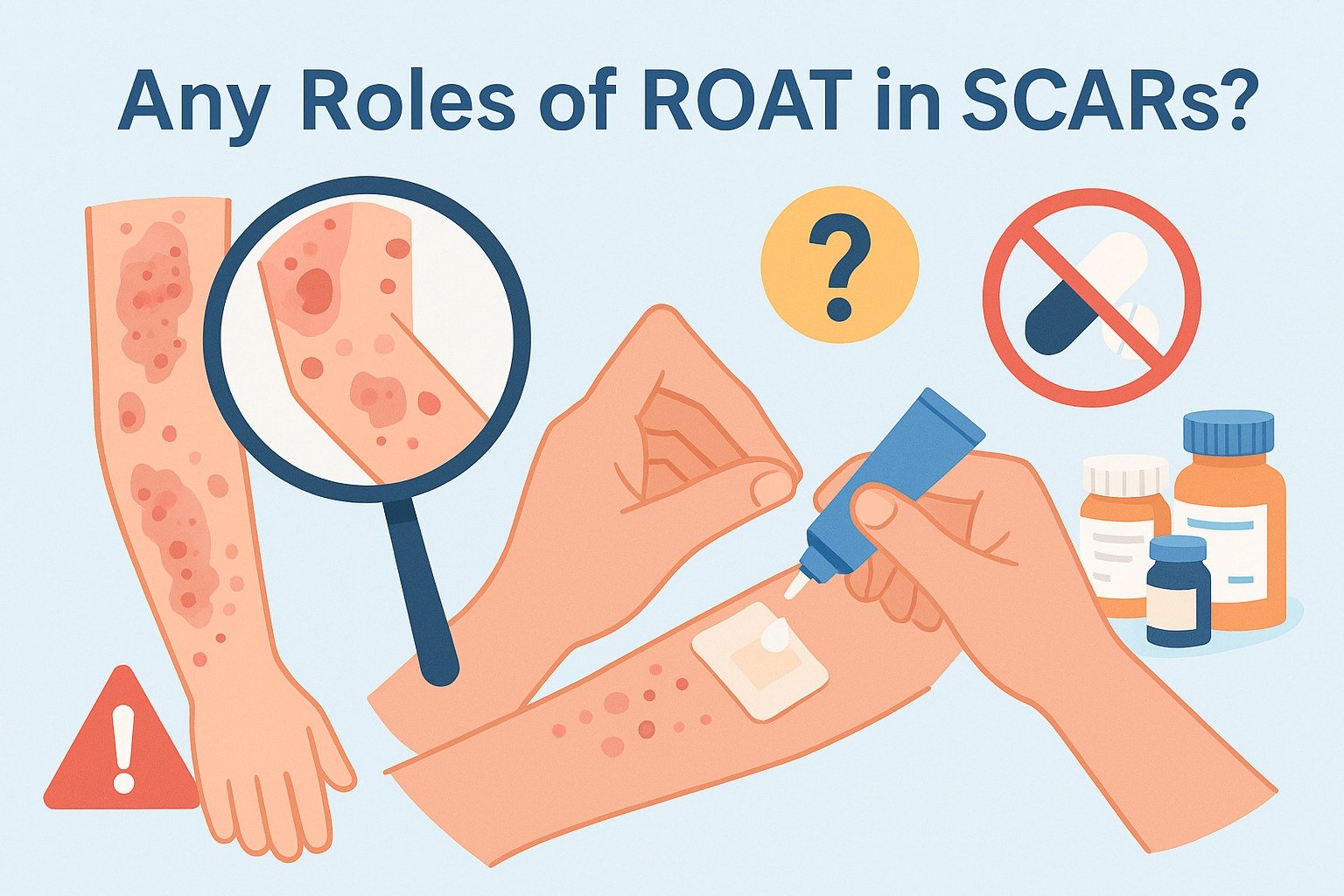
Read MoreROAT Patch Testing in SCARs: Is It Time to Reconsider?
Introduction Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs) — such as DRESS, AGEP, and SJS/TEN — are among the most serious drug hypersensitivity syndromes.The traditional approach is simple: avoid all suspected drugs indefinitely. But this blanket avoidance often creates real-world problems: This raises an important question:👉 Is it time to reconsider the role of patch testing — and even the Repeated Open Application Test (ROAT) — in managing SCARs? Why ROAT Is Feared in SCARs The Repeated Open Application Test (ROAT) is a simple diagnostic tool in delayed hypersensitivity: Concerns in SCARs:…
Read MoreFDA Warns of Severe Rebound Itching After Stopping Cetirizine (Zyrtec) or Levocetirizine (Xyzal): What You Need to Know
🛑 New FDA Safety Alert: Antihistamine Withdrawal Can Trigger Severe Itching In May 2025, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a new safety warning about rebound itching after stopping cetirizine (Zyrtec) or levocetirizine (Xyzal)—two of the most commonly used antihistamines. This severe itching reaction, often mistaken for allergy relapse, may occur especially in people who have taken the drug daily for several months. 🔎 Key Findings from the FDA Investigation Between April 2017 and July 2023, the FDA identified 209 confirmed cases globally—197 in the U.S.—involving moderate to…
Read MoreWhen and How to Perform Drug Provocation Tests in Drug Hypersensitivity: Timing Matters
Introduction Drug provocation test timing plays a critical role in evaluating suspected drug allergies. Drug provocation testing (DPT), also known as a drug challenge, remains the gold standard for confirming or ruling out drug hypersensitivity. However, success depends heavily on understanding how soon after drug exposure symptoms appear. By tailoring the timing and protocol of DPT based on the type of reaction—immediate, delayed, or severe—clinicians can improve diagnostic accuracy and minimize risk. This post outlines practical strategies, guideline updates, and real-world challenges that affect how and when drug provocation tests…
Read MoreRethinking Drug Allergy Management: Finding Balance Between Caution and Access in SCARs
Drug allergies present a complex landscape, demanding tailored management strategies based on the reaction’s nature and severity. We’ve witnessed significant progress in “de-labeling” allergies to common drugs like penicillin through careful testing, allowing many to safely access essential treatments. However, the approach to severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs) – encompassing Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), and Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP) – often stands in stark contrast: a broad and often indefinite avoidance of all potentially implicated drugs. While the…
Read MoreReevaluating the Approach to Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs): Is Drug Rechallenge Always Off the Table?
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs), such as acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), are among the most feared drug-related complications. These conditions can result in devastating outcomes, and the conventional approach to managing SCARs emphasizes strict avoidance of the suspected culprit drug to prevent potentially fatal recurrences. But is avoidance always the only path forward? Could there be room for a more nuanced strategy in specific cases? Not All SCARs Are Created Equal SCARs represent a spectrum of disorders,…
Read MoreUnderstanding Aspirin and NSAID Hypersensitivity: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
Introduction to Aspirin (ASA) and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Aspirin (ASA) and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are among the most widely utilized medications in the world, renowned for their efficacy in alleviating pain, reducing inflammation, and lowering fever. Aspirin, extensively studied since its introduction in the late 19th century, is also acclaimed for its cardiovascular benefits, particularly in preventing heart attacks and strokes. NSAIDs, which include ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac, offer similar therapeutic effects and are indispensable in managing a range of conditions from acute injuries to long-term issues like…
Read MoreNew Sequential Patch Testing for Fixed Drug Eruption (FDE) Diagnosis
Background Fixed drug eruption (FDE) is a cutaneous adverse drug reaction characterized by erythematous plaques or blisters that recur at the same site upon re-exposure to the causative drug. It can leave residual pigmentation and, in severe cases, may present as generalized bullous fixed drug reaction (GBFDE). Objective The study aimed to evaluate the sensitivity of a standardized allergy workup for diagnosing the cause of FDE, with an emphasis on in situ repeated open application tests (ROATs). Methods A retrospective multicenter study analyzed the allergy workup practices for FDE diagnosis…
Read MoreDrug Allergy Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
Available Drug Allergy Skin Tests Drug allergy skin tests play a crucial role in diagnosing potential allergic reactions to medications. Among the most common tests are the prick test, intradermal test, and patch test. Each of these tests has specific methodologies, applications, and diagnostic capabilities. The prick test, also known as a scratch test, is frequently used to identify immediate allergic reactions. During this test, a small amount of the suspected allergen is placed on the skin, usually on the forearm or back, and the skin is lightly pricked with…
Read More